What is a bad credit score?
Several factors lead to a bad credit score, such as delayed payments and carrying a balance on your credit card. Identifying and rectifying the factors that harm your credit score and credit report is necessary.
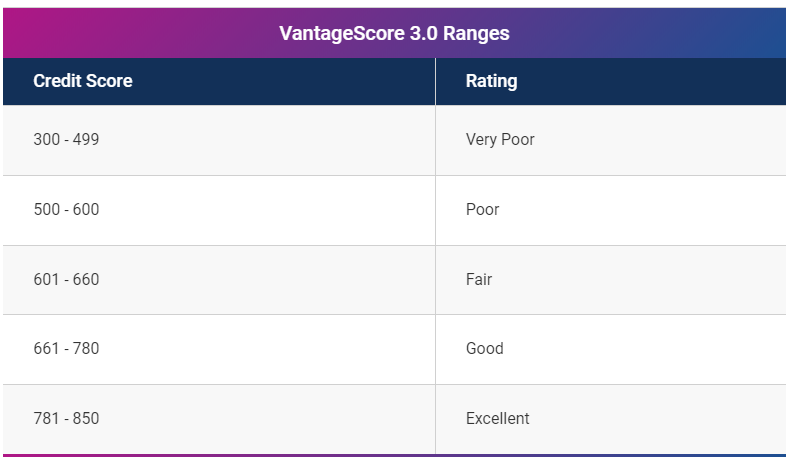
A bad credit score usually falls under 580 in the 300 to 850 range and is based on the details in your credit report. It is harder for those with bad credit to acquire loans or apply for a new credit card as lenders need to know how likely you will repay them with interest.
In the FICO scoring model, a bad score is that which falls below 670. Read more to discover how to improve your credit to the good credit score range, i.e., 700 or higher in the 300 to 850 range.
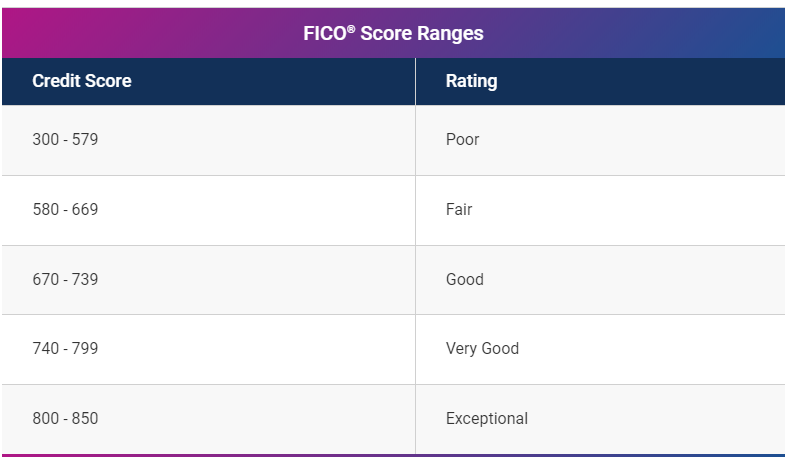
Another scoring model, the VantageScore, uses a score range of 300 to 850 to determine whether you have a good or bad credit score. Designed by the three major credit bureaus (Equifax, TransUnion, and Experian), a 601 – 660 score is reviewed as fair, whereas scores varying from 300 to 500 are considered poor.
You can easily qualify for credit at better terms and interest rates with a good credit score. It is difficult to acquire credit at affordable rates and qualify for a loan or credit card with a low credit score.
With bad credit, you may face the following hurdles:
● Rejection when applying for lines of credit or loans such as mortgages, auto loans, personal loans, student loans, and credit cards.
● Struggle with getting a rent application accepted. Bad credit affects non-lending decisions, like if a landlord agrees to lease you a house or apartment after evaluating your credit report and payment history.
● You may be required to make a security deposit before moving into a new place for utilities like electricity, water, and gas.
● Many cell phone providers will check your credit before catering to you to see how likely you will pay bills on time.
● Employers may look at your credit report before recruitment or making any promotional decisions to evaluate your financial management skills. They will closely look at the activities that lead to a poor credit score, like skipping or delaying payment.
● Insurance companies also use insurance scores based on your credit to determine how much you can pay for auto, home, and life insurance premiums.
How You Can Improve a Bad Credit Score
Credit scores change with the shift in information in your credit report. This means you can manage your financial status and do activities to enhance your credit score.
Take the following approaches to improve your bad credit:
1. Assess Your Free Credit Score
Inspect your credit score free of cost to assess the factors affecting it.
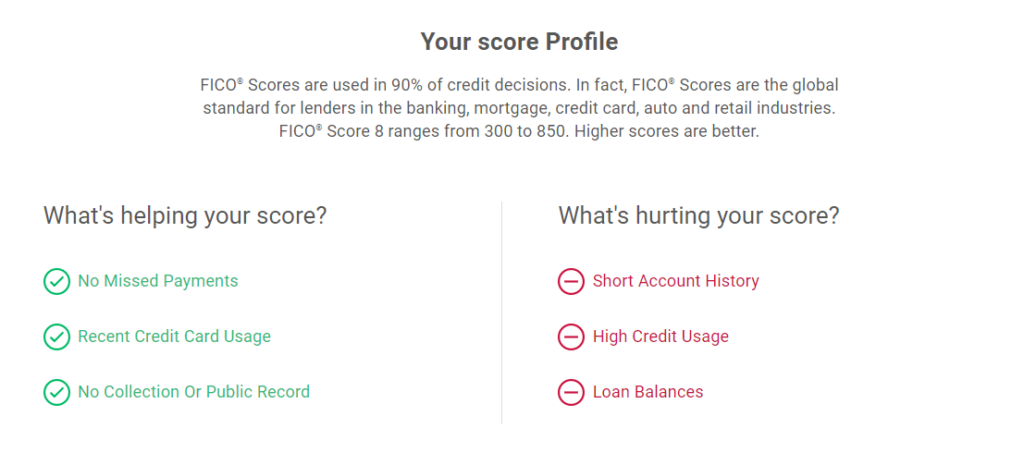
The following factors have the most impact on your credit score:
● Payment history – 35%
● Total available credit and how much is being utilized – the credit utilization rate – 30%
● Duration of credit usage – 15%
● Credit mix – Installment or revolving accounts – 10%
● Latest activity and recent credit accounts. Opening a new account can lead to hard inquiries, which may pull your credit score low – (10%).
It is advised to check your credit report for any erroneous entries and dispute the negative information with credit bureaus. Fixing errors such as incorrect personal information or fraudulent accounts opened in your name will positively influence your credit score.
3. Make timely payments
Your payment history accounts for 35% of your FICO Score. Establish an autopay system for recurring payments such as bills, student loans, and auto loans. Make sure your current account has sufficient finances for payments, or you could be subjected to extra charges for late payment.
Contact your lender or creditor to know more about alternative payment plans that decrease the amount you have to pay monthly for student loans.
Banks or credit card unions might lower your payment or interest rate till some time if you are facing any financial constraints.
Debts amount to 30% of your FICO Score, making it the next biggest allotment second to payment history. It is recommended to utilize a maximum of 30% or below the allowed credit limit.
Pause utilization of your credit cards and make partial debt payments (pay down debt) if you cannot pay off your credit card in full every month and are carrying a balance. Using the “debt avalanche” method for paying debt payments will save you the most money in interest.
Another way to pay off small amounts is by using the debt snowball method, which motivates you to knock off each remaining balance as you gain momentum.
Opt for a ‘balance transfer credit card’ if more time is needed to bring your balances down. This card allows you to pay off your remaining balances interest-free without making additional payments over time.
4. Steer Clear of New Hard Inquiries
You might want to keep away from or postpone applying for new credit if you look to improve your credit score, as hard inquiries may affect your score. Lending institutions examine your credit report in order to evaluate and determine your financial capability of repaying the amount borrowed. Moneylenders consider those who apply for loans from several institutions a great credit risk. New credit account requests amount to 10% of your FICO Score.
Checking your credit score is also a soft inquiry on your credit report, which does not affect your score. Credit card lenders may also review your report to approve you for certain services.
Applying for only one car loan or mortgage with several issuers in a short period will not significantly affect your credit score.
5. Upheave Your Credit
Another way to build up your credit with your current financial history is by using Experian Boost. After signing up free of cost, Experian will browse through your account information for utility, telephone, and cable clearances. You have the liberty to pick which accounts to connect to your credit portfolio. Adding the selected accounts will instantly generate your new credit score.
The new beneficial payment history may increase your FICO Score, especially if you have low or poor credit.
6. Seek Assistance With Building Credit
Positive credit history can be built with the help of credit counseling agencies or a secured account if you cannot receive approval for a new credit card or loan.
Undertake the following strategies:
● Turn into an authorized user on an account that does not belong to you.
● Get a cosigner with good credit to assist you with applying for a loan or a new credit card. Cosigners are equally responsible for the repayment of a debt.
● Activate a secured account. The credit card issuer permits you to borrow an estimated percentage of the amount deposited in your account.
Bottom Line
Knowing your vantage point regarding your financial status is perhaps the most integral factor in the drive to increase your credit score. Master your financial well-being by frequently checking your credit report using free online services like Experian.
There are solid actions that can be taken to improve a bad credit score and keep it as high as possible.






